Atirmociclib (PF-07220060)
Atirmociclib | PF-07220060 is an investigational compound. Its safety and efficacy have not been established.
Overview + Rationale
RATIONALE FOR CANCER TARGET
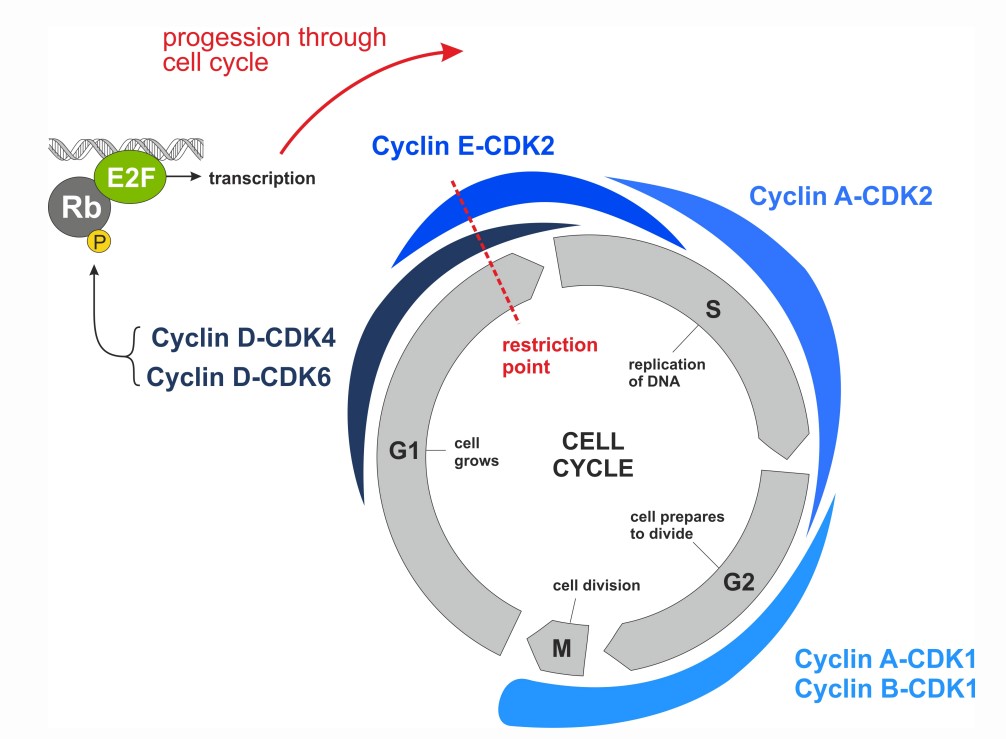
- Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) play important roles in the control of cell division and modulate transcription in response to several extra and intracellular cues
- The cyclin D–CDK4/6–retinoblastoma (Rb) pathway plays a key role in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Phosphorylation of Rb and subsequent E2F-mediated transcription are required for G1 cell-cycle progression
- Aberrations in the cell-cycle have been implicated in human cancer pathogenesis
OVERVIEW
The Rb tumor suppressor protein plays a pivotal role in the negative control of the cell cycle. It is responsible for a major G1 checkpoint, blocking S-phase entry and cell growth. Phosphorylation leads to functional inactivation of Rb. Loss of Rb cell cycle–suppressive functions can be mediated through multiple mechanisms: loss of Rb, increased signaling through CDK4 & 6 amplification, overexpression or aberration of cyclin D/E, and loss of the inhibitory function of gene products, such as CDKN2A/B the latter leading to CDK4/6 activity.
Mechanism of Action
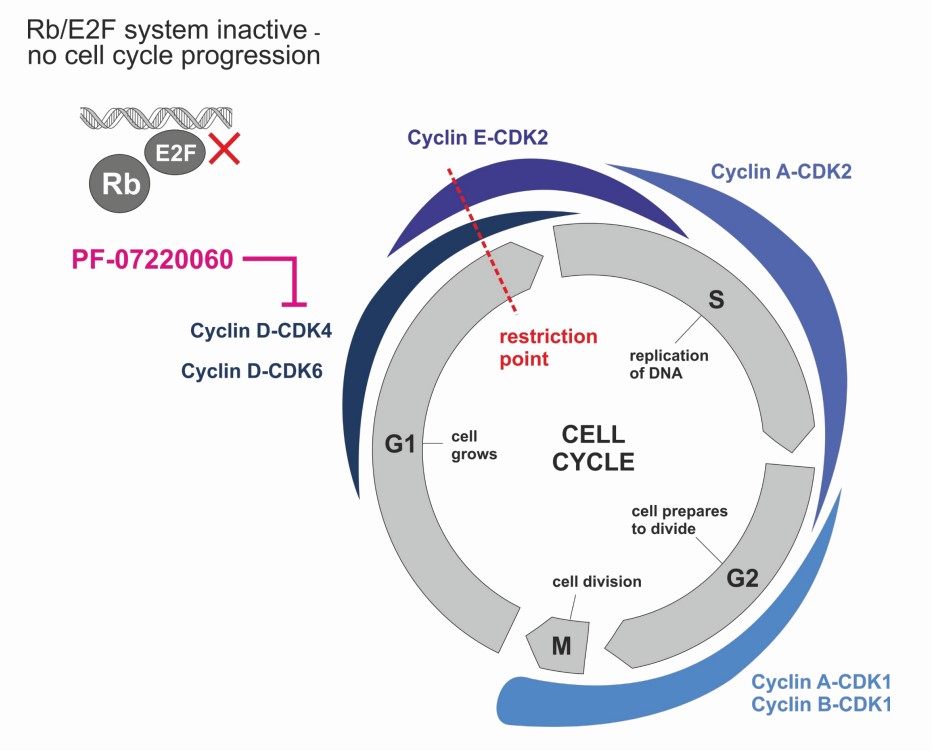
- Atirmociclib | PF-07220060 is a selective CDK4 inhibitor with potential antineoplastic activity in several solid tumors
- Atirmociclib | PF-07220060 inhibits the CDK4/cyclinD complex and renders the Rb/E2F transcription system inactive
Inhibition
Stage of Development
Advanced or Metastatic Solid Tumors
HR+/HER2- Metastatic Breast Cancer
Phase 1/2A Monotherapy and Combination
Phase 1b/2 Combination*
(1L) Phase 3 Combination
(2L) Phase 2 Combination*
Prostate Cancer


 Back
Back


