Integrin alpha-V/beta-8 Antagonist
PF-06940434 is an investigational compound. Its safety and efficacy have not been established.
Overview + Rationale
- Integrins are cell-surface adhesion molecules that mediate cell–cell, cell–extracellular matrix, and cell–pathogen interactions. In mammals, 24 different integrins are formed by specific, noncovalent association of 18 α-subunits with 8 β-subunits
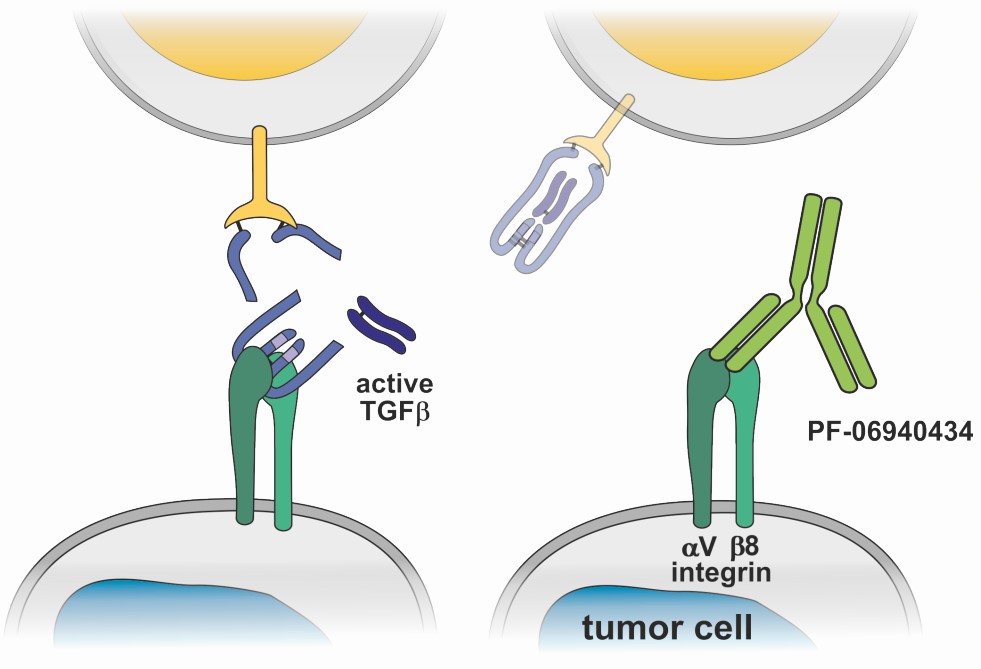
- Integrins αVβ6 and αVβ8 are specialized for binding to and releasing TGF-β from its surrounding LAP prodomain, thereby activating it
- In many solid tumors, the immunosuppressive TGF-β pathway is associated with poor prognosis. TGF-β is thought to promote tumor development via proliferation, immune cell exclusion and inhibition of function and suppressive immune cell differentiation
- Recent studies suggest that increased TGF-β activity in tumor stroma is thought to prevent tumor penetration by cytotoxic CD8+ T cells and may prevent response to PD-L1 inhibitors
- Integrin αvβ8–expressing tumor cells thus evade host immunity by regulating TGF-β activation in immune cells and could be a potential oncology target
- PF-06940434 is an antagonist of integrin alpha-V/beta-8 (αvβ8)
Mechanism of Action
By blocking integrin aVβ8, in preclinical studies, PF-06940434 inhibited the release of active TGFβ1 & 3 into the tumor microenvironment
Stage of Development
Advanced or Metastatic Solid Tumors
Phase 1 Monotherapy and Combination*

 Back
Back
