Sigvotatug vedotin
Sigvotatug vedotin is an investigational compound. Its safety and efficacy have not been established
Overview + Rationale
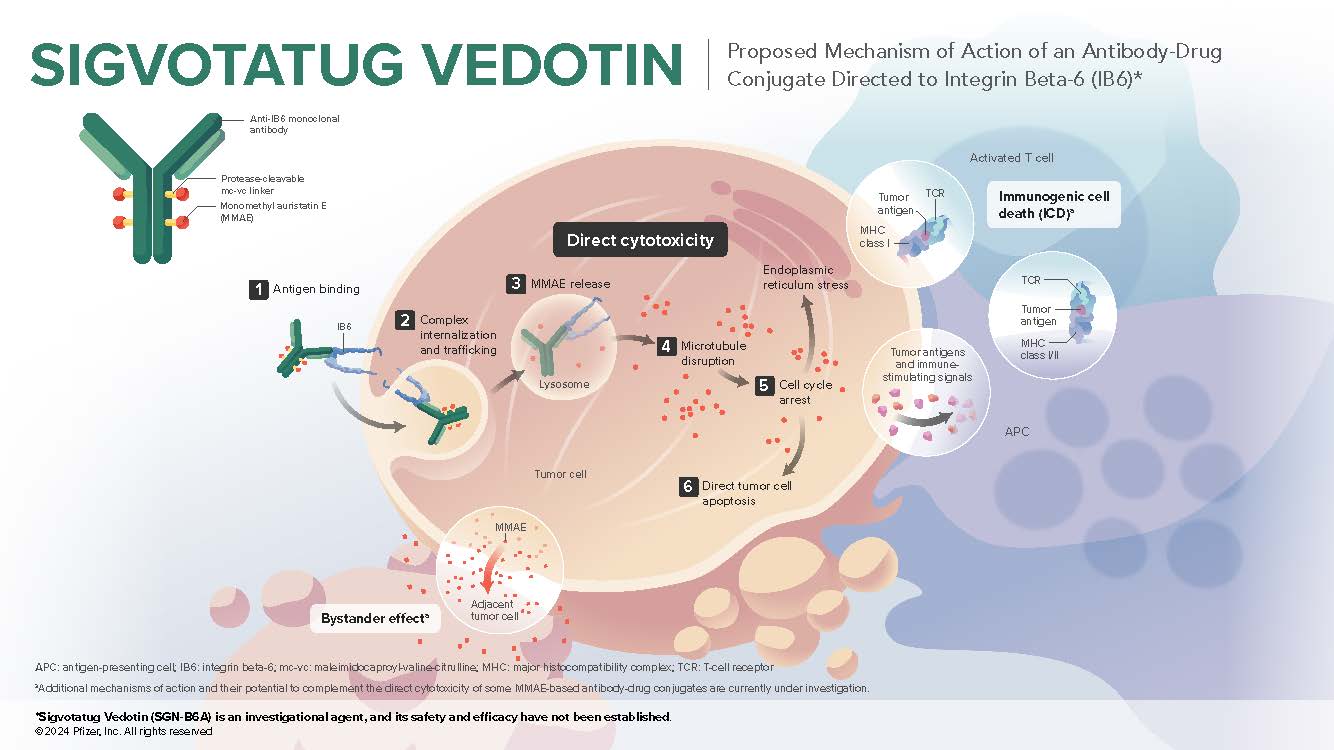
Sigvotatug vedotin is an investigational antibody-drug conjugate composed of 3 components: a monoclonal antibody directed to IB6 (integrin beta-6), a microtubule-disrupting agent MMAE (monomethyl auristatin E), and a protease-cleavable mc-vc (maleimidocaproyl-valine-citrulline) linker that covalently attaches MMAE to the antibody, which enables preferential release of MMAE within target cells1
IB6 is a cell surface receptor that promotes cellular adhesion through interactions with the extracellular matrix, which plays a major role in solid tumor pathogenesis and invasiveness2,3
IB6 expression is normally low but is highly upregulated during pathogenesis4-6
IB6 is expressed in numerous solid tumors including non-small cell lung cancer, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, esophageal cancer, and cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma1,7-9
IB6 is a proposed negative prognostic marker based on multiple analyses9,10
Mechanism of Action

 Back
Back

