Sasanlimab
Sasanlimab is an investigational compound. Its safety and efficacy have not been established.
Overview + Rationale
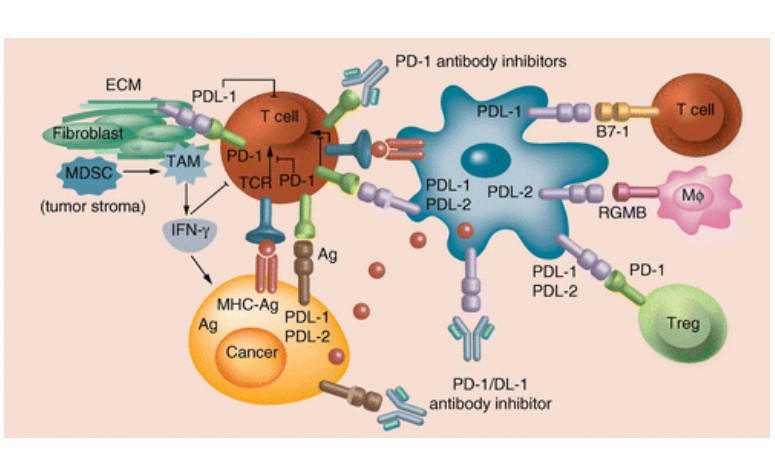
- Programmed death-1 (PD-1) is a protein that belongs to the CD-28 family and is expressed on T cells, dendritic cells, natural killer cells, macrophages, and B cells
- PD-1 functions as an immune checkpoint that negatively regulates T-cell activation and effector function when activated by its ligands, and may play an important role in tumor evasion from host immunity
- Sasanlimab is a humanized immunoglobulin G4 monoclonal antibody that binds PD-1 to block its interaction with PD-L1 and PD-L2
- Sasanlimab is administered by subcutaneous injection (SC)
Mechanism of Action
- PD-1 is an immune checkpoint receptor, which mainly expresses on activated T, B, dendritic (DCs), natural killer (NK), and Treg cells
- On the surface of activated T cells, PD-1 expression is upregulated after the recognition of peripheral antigens by T cells; subsequently, the elevated binding of PD-1 to PD-L1 becomes a key step for downstream inhibitory signaling
- PD-1 is also associated with increased Treg-cell proliferation and enhanced immunosuppressive function
Stage of Development
Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
Advanced Malignancies/Solid Tumors
Phase 1 Combination

 Back
Back


